How a Halogen Light Bulb Works

What is a Halogen Light Bulb?
A halogen light bulb (also known as a halogen lamp) is a specialized incandescent light that contains halogen gas inside the glass casing. The gas causes a chemical reaction that constantly “recycles” the tungsten material within. This makes halogen bulbs a longer lasting and more energy-efficient update of regular incandescent bulbs.
Halogen bulbs come in different shapes, sizes, and bases. Here’s a rundown of how it works and what to expect when using one.
Why Were Halogen Bulbs Invented?
The story of the halogen lamp begins over 100 years ago, when Thomas Edison invented the incandescent bulb. Simple, elegant, and cheap, it quickly became the standard way to turn electricity into light. In the design, a glass bulb encloses a small wire (called a filament) which glows when electricity is passed through it. The filament is made of tungsten, a strong and resilient metal that can take the high heat without falling apart. And, because there is no oxygen inside the glass, it doesn’t burn up.
There is a catch with incandescent bulbs, however. Even though the filament doesn’t burn in the sense of catching on fire (If it does, you’ve got another problem on your hands!) due to the electricity being conducted, the extreme heat required for incandescence causes the bulb to undergo a form of evaporation. And this buildup results in making the filament gradually grow thinner and thinner. Soon enough, the evaporated tungsten ends up on the glass as a visible dark spot.
After about 750 to 1000 hours of use, the filament eventually gets so thin that it breaks, which is what happens when your light bulb “burns out.” But, with the invention of the halogen bulb, there is a new solution to illuminate your space without some of the complications of incandescent bulbs.
Enter the halogen design update. A halogen lamp is a particular sort of incandescent bulb, with a few key differences from the standard design.

What Makes Halogen Bulbs More Energy Efficient?
While a halogen also uses a tungsten filament, instead of a glass bulb, the filament is enshrouded in a smaller quartz “envelope.” Inside the quartz envelope is a halogen gas which has a special property: It is able to combine with tungsten vapor. At a high enough temperature, the evaporating tungsten combines with the halogen gas, which redeposits the tungsten onto the filament again.
So essentially, a halogen light bulb has its own recycling program. This enables a halogen light bulb to last two to three times longer than a regular incandescent light bulb. In addition, the quartz envelope can withstand much higher temperatures than glass, so a halogen light bulb can run hotter and therefore produce more light.
3 Advantages of Halogen Bulbs over Standard Incandescent Bulbs
- Last two to three times longer than standard incandescent bulbs.
- Smaller in size than standard light bulbs.
- Capable of producing brighter light than standard incandescent designs.
These advantages make halogens the bulb of choice for a wide range of applications, from kitchen and bath lighting to reading lights, desk lamps, chandelier light bulbs, and more.
What Are the Most Common Halogen Lamp Types?
Halogen bulbs often come as short tubular forms, mini-reflectors, and wider PAR reflectors.
While halogens can come in many shapes and sizes, these are the most halogen lamp types that you will find.
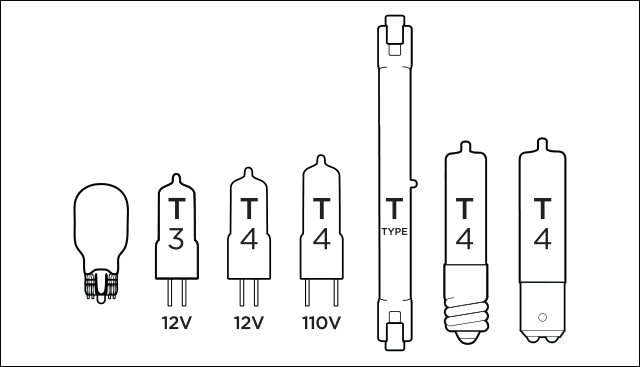
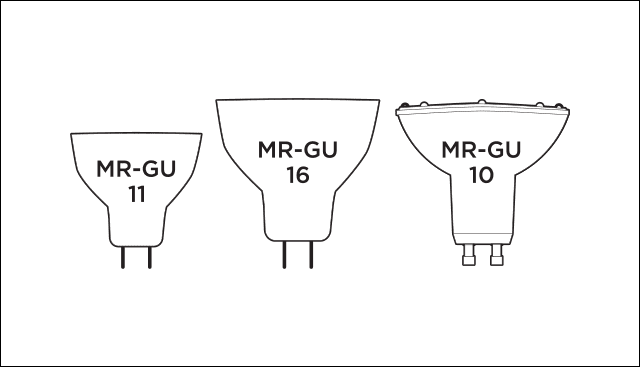
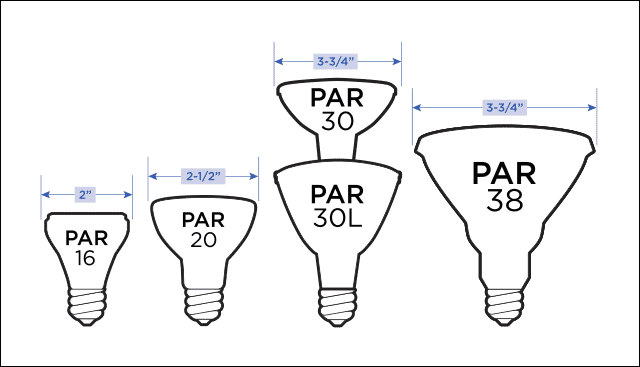
Handling and Replacing Halogen Bulbs
While changing out a halogen is easy, there is a key rule to keep in mind from the moment you remove your bulb from the package that will ensure a longer lifespan from the beginning. You should never touch a halogen light bulb with your bare hands.
Sounds strange, doesn’t it? Well, there is actually good reason to avoid contact with the surface of the bulb. The oils on your fingers and skin can damage the quartz glass which creates a hot spot on the surface of the bulb when illuminated.
The localized heat on the surface works just like oil in a pan, and these hot spots can weaken the bulb’s glass, allowing the essential gasses we explored earlier to leak out. Even worse, the compromised integrity of the bulb can allow for it to explode.
Because of this, we always recommend that halogen bulbs never be handled by your bare hands. Use gloves or clean paper when holding the bulb so that you do not make immediate contact. Also, because these bulbs burn at a high temperature, make sure you let any bulbs you are replacing cool down before removing them.
Now you know all there is know about halogen lamps! Check out our full selection of halogen light bulbs here.
And if you have time, check out the links below to find out about other types of light bulbs, particularly other energy efficient light bulbs.
More Light Bulb Ideas and Advice
Lumens to Watts: the Key to Buying Replacement Light Bulbs
Light Bulb Identifier and Finder Guide
